All about the Nifty Bank Index and reasons you should invest in it?

Banking Sector in India
Banking sector is the backbone of any economy. Banks provide an ecosystem to carry out financial transactions. Companies depend on bank loans to fund their working capital and capex. Economic growth of a country is dependent on a robust and well-functioning banking system. The Indian banking system comprises of 138 scheduled commercial banks – 12 public sector banks, 21 private sector banks, 44 foreign banks, 43 regional banks, 10 small finance banks, 6 payment banks and 2 local area banks. In addition to scheduled commercial banks we also have cooperative banks (source: RBI).
The Government has taken a number of steps to reform and strengthen the banking sector. The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana aimed at providing financial inclusion to all Indians has brought nearly 53 crore Indians under the banking system with Rs 228,637.82 crore balance in beneficiary accounts (source: Ministry of Finance as on 31st May 2024). The Government has also enacted a number of reforms for public sector banks including mergers, recapitalization, recognition of NPAs and recoveries. The Government has made a major thrust for digitization of payments through the Jan Dhan, Aadhaar and Mobile (JAM) trinity. Unified Payments Interface (UPI) recorded 14 billion transactions in May 2024, valued at Rs 20 trillion (source: NCPI, as on 31st May 2024).
Nifty Bank Index
Nifty Bank Index comprises of 12 large and liquid banking stocks. Nifty Bank Index is a market cap weighted index, which means that the stocks with higher free floating market capitalization has higher weights in the index. The chart below shows the constituents of Nifty Bank Index
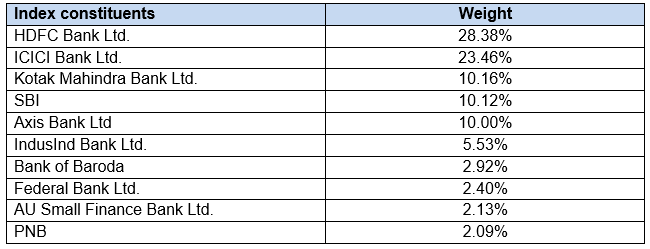
Source: NSE Factsheet, 28th June 2024
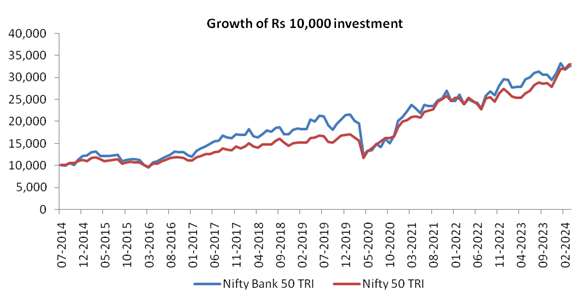
Performance of Bank Nifty Index
Bank Nifty TRI has outperformed Nifty 50 TRI over long investment horizon (see chart below).
Why invest in Nifty Bank Index?
India is in a macro sweet spot both in terms of GDP growth and on the right trajectory towards fiscal consolidation. IMF is forecasting India’s GDP to grow by 6.8% in FY 2025, making it the fastest growing G-20 economy. India’s fiscal deficit in FY 2023-24 is estimated to be 5.8% and will be pared down to 5.1% in FY 2024-25. The Government expects the fiscal deficit to be back to the long term 4.5% of GDP target by FY 2025-26.
Interest rates have peaked and the market is expecting interest rate cuts later this year. Lower interest rates may spur consumer demand and capex spending, which lead to credit growth and higher revenues / earnings for the banking sector. The banking sector usually reflects the economic growth of the country. IMF has forecasted India to be the 3rd largest economy by 2028. Banking sector will have an important role to play in the long term India Growth Story.
Active versus passive investing in banking sector
- TER or the Total Expense ratios of Index funds or ETFs like the Nifty Bank Index /ETFs are much lower than actively managed funds. The fund manager of actively managed funds has to generate higher alphas on a regular basis to match the performance of index funds. Over long investment horizons the lower costs can result in considerable higher returns due to the effect of compounding returns.
- The Index funds investment strategy & stock selection is simple, transparent and clearly defined, Stocks are held as per the underlying index in the same weights. The performance of the fund will track the performance of the index subject to tracking error which depends on factors like TER, cash held by the fund etc.
- The fund manager of an active fund generally goes overweight or underweight on certain stocks in the benchmark. This could result in stock or sector specific unsystematic risks. Unsystematic risks can either lead to outperformance as well as underperformance. In the case of index funds and ETFs there is no unsystematic risks.
- Fund managers are humans and are prone to human errors in judgement. This could have an impact on the performance of the schemes managed by them. Furthermore, change in fund manager can have an impact on the performance of an active scheme. There is no human or fund manager bias in index funds – they simply track the index.
How can you invest in the Nifty Bank Index?
You can choose to invest in the bank Nifty Index directly through the Exchange Traded Funds (ETF) or as Mutual Fund investments. Both ETFs and Index mutual funds are passive funds, which invest in a basket of securities which replicate a particular market index, in this case the Bank Nifty Index. In you want to invest in Bank Nifty ETFs you need to have demat and trading accounts. You can buy / sell Bank Nifty ETF units only in stock exchanges at prevailing intraday market prices through your trading account, unless you are transacting in lot sizes (creation units).
If you do not have demat account, then you can invest in Bank Nifty Index funds. Index funds are mutual fund schemes and offer the convenience of mutual funds. You can buy / redeem units of your index with the asset management at prevailing Net Asset Values (NAVs), either directly or through your mutual fund distributor. You can invest index funds from your regular savings through Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs). Both ETFs and index funds are suitable options for investing in Nifty Bank ETFs. You should decide based on your personal situation and investment experience.
Who should invest in the Nifty Bank Index?
Investment in Bank Nifty Index is suitable for the following investors:
- Those investors who have an investment goal of capital appreciation over long investment tenures
- The fund is suitable for investors with very high-risk appetites
- Those investors who are looking for a single sector exposure in the banking stocks.
Contact your mutual Fund distributor or financial advisor to understand how Bank Nifty Index can add extra diversification to your equity portfolio.
Mutual Fund Investments are subject to market risk, read all scheme related documents carefully.
Axis Mutual Fund launched its first scheme in October 2009 Since then Axis Mutual fund has grown strongly. We attribute our success thus far to our 3 founding principles - Long term wealth creation, Outside in (Customer) view and Long term relationship. Come join our growing family of investors and give shape to your desires.
Quick Links
Other Links
Follow Axis MF
POST A QUERY





