Dividend Yield Funds: SBI Dividend Yield Fund NFO

What is dividend?
The profit made by a company from its operations is known as the operating profit or in accounting terms, EBITDA (Earnings before Interest, Depreciation and Amortization). From EBITDA, the company pays interest to its lenders. Depreciation and amortization, which are non-cash items, are also deducted from the EBITDA. Depreciation and amortization are shown as expense because the book value of the fixed assets of the company e.g. plant and machinery reduces over its useful life. The profit after deducting interest, depreciation and amortization is known as profit before tax (PBT). If the company makes a profit before tax, then it has to pay corporate tax. A portion of the profit after tax (PAT) is retained by the company as Reserves & Surplus and a portion can be distributed to shareholders as dividends at the discretion of the management. Instead of paying dividends to shareholders, the company can also buy back (repurchase) the shares from shareholders. Share buyback or repurchase is a type of dividend because the share price of the company will go up when the company buys back shares.
What is dividend yield?
Dividend yield is the annual dividend paid by the stock divided by the share price. Dividend yield is an important ratio in selecting stocks. Dividend yield = (Annual dividends ÷ Current share price). Suppose the share price of a company is Rs 100. The company declares a dividend of Rs 10. The dividend yield will be Rs 10 ÷ 100 = 10%.
Which is good – high or low dividend yield?
The two primary objectives of investment are capital appreciation and income. Companies which distribute a lower percentage of the PAT as dividends are able to build their reserves and surplus faster, which can be re-invested in the business to grow the PAT and earnings per share (EPS) of the company. High EPS growth stocks have higher capital appreciation.
Dividend, on the other hand, is income for the shareholder. High dividend yield stocks also are more suitable for investors who do not have high risk appetites. Stocks which pay high dividends are essentially returning a portion of the capital to the investor on a periodic basis. Through the length of the investment tenor, investors’ risk in high dividend yield stocks reduces over time as a portion of the investment is paid back to the investor in form of dividends, leaving a smaller portion at market risk.
Why is dividend yield important?
Key attributes of high dividend yield stocks are:-
- Relatively morematured businesses with an ability to generate healthy free cash flows.
- Relatively less prone to downside risk in falling market coupled withcapital appreciation prospects in a reviving market.
- Reflects optimum usage of free cash flows, good operational health & sustainability of future earnings.
- Consistent dividend pay outs & growth ora possibility of likely growth in dividend pay-outs.
Dividend yield funds in volatile markets
Dividend yield funds are equity mutual fund schemes which invest in high dividend yield stocks. High dividend yield stocks provide margin of safety to investors when the market turns volatile, since investors receive cash-flows in form of dividends even when the share price corrects (falls). This not only reduces your downside risks; you can re-invest in the dividends when share prices are falling and have the potential of getting higher returns when market recovers.
The chart below shows how high dividend yield stocks were able to limit downside risks in large market drawdowns.
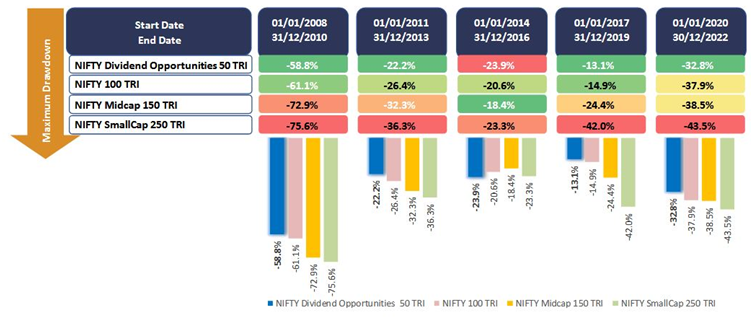
Source: SBI MF
Dividend yield funds can also outperform in stages of market recovery
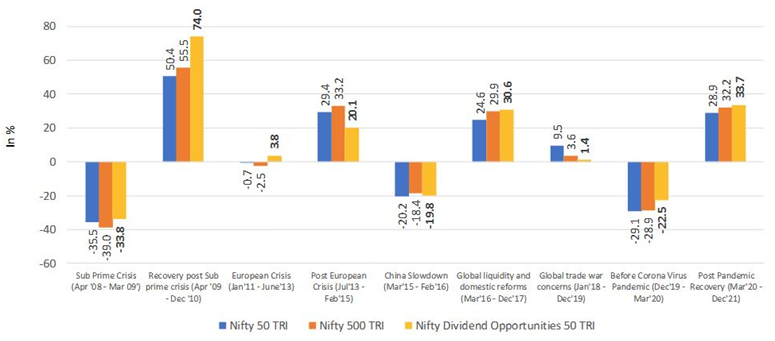
Source: SBI MF
Misconceptions about dividend yield stocks demystified
- Dividend yield stocks are only very large, bluechip companies - Strategic/ tactical opportunities amongst consistentdividend paying companies that may exist across the market cap spectrum at different points in time.
- Dividend yield stocks have low EPS growth potential - Dividend companies with stable cash-flows also havethe potential for long-term growth compounding.
- Investing in dividend yield stocks is same as value investing - Dividend yield companies with potential to growdividends over time can be growth oriented coupledwith an ability to return cash to shareholders.
SBI Dividend Yield Fund NFO
SBI Mutual Fund is launching a New Fund Offer SBI Dividend Yield Fund. The NFO opens for subscription on 20th February 2023 and will close on 6th March 2023. The salient features of the scheme are as follows:-
- SBI Dividend Yield Fund is a diversified equity mutual fund scheme which will invest across industry sectors and market capitalization segments.
- SBI Dividend Yield Fund will invest in dividend paying companies and endeavour to construct aportfolio such that the aggregate dividend yield is at least 50% higher than that ofthe Nifty 50 Index.
- SBI Dividend Yield Fund will consider dividend yielding stocks which have paid dividend or repurchased its shares in at least one of the three preceding financial years.
- SBI Dividend Yield Fund will invest in stocks with potential growth individends
Why invest in SBI Dividend Yield Fund now?
- Global inflation has been stickier than previously anticipated. This may force central banks to increase interest rates more than previously anticipated by the market or keep them elevated for a longer period of time than previously anticipated.
- Since the inflation and interest rate outlook is uncertain, the market may continue to be volatile for some time. Since India was an outperformer in 2021 and valuations seem stretched we may see volatility affecting some stocks.
- As such, a stock specific approach with focus on high dividend yields may be suitable in the current environment.
- There is increased focus of large investorcommunity towards companies with stable and optimum freecash-flows. Dividends reflect sustainablefuture performance & long-termgrowth visibility.
- Propensity to pay dividends is well aligned with improvingcorporate governance. As such, dividend yield funds have an intrinsic focus on high quality and sustainability.
Who should invest in SBI Dividend Yield Fund?
- The scheme is suitable for new or existing investors looking forpotential long term wealth creation wanting to have exposure torelatively strong businesses. The scheme is suited for new investors because volatility will be relatively low.
- The scheme is also suitable for long term investors aimingto build wealth to meet their long term financialgoals with a potentiallybetter risk return trade off.
- The scheme may also be suitable for investors who want regular tax efficient cash-flows from their investments through Systematic Withdrawal Plan (SWP) over long investment horizons.
- Investors should have minimum 4 years plus investment tenure for this scheme.
Investors should consult with their financial advisors or mutual fund distributors, if SBI Dividend Yield Fund is suitable for their investment needs.
Mutual Fund Investments are subject to market risk, read all scheme related documents carefully.
Queries
-
What is the benefit of mutual fund STP
Aug 29, 2019
-
How much to invest to meet target amount of Rs 2 Crores
Aug 26, 2019
-
Can I achieve my financial goals with my current mutual fund investments
Aug 24, 2019
-
Can you tell me return of various indices
Aug 19, 2019
-
What would be the post tax return on different investments
Aug 18, 2019
-
Which Principal Mutual Fund scheme will be suitable for my retirement corpus
Aug 16, 2019
-
What is the minimum holding period for availing NCD interest
Aug 4, 2019
Top Performing Mutual Funds
Recommended Reading
Fund News
-
Zerodha Mutual Fund launches Zerodha Nifty Short Duration G Sec Index Fund
Dec 26, 2025 by Advisorkhoj Team
-
Groww Mutual Fund launches Groww Nifty Chemicals ETF
Dec 26, 2025 by Advisorkhoj Team
-
DSP Mutual Fund launches DSP Nifty Next 50 ETF
Dec 19, 2025 by Advisorkhoj Team
-
DSP Mutual Fund launches DSP Nifty 500 Index Fund
Dec 19, 2025 by Advisorkhoj Team
-
Kotak Mahindra Mutual Fund launches Kotak Nifty Next 50 ETF
Dec 18, 2025 by Advisorkhoj Team