The time for Hybrid is here: Why is it important to make hybrids part of your portfolio?

What is asset allocation?
Asset allocation refers to diversification of your investments across different asset classes e.g. equity, fixed income, commodities, international equities etc. The old proverb, “do not put all your eggs in one basket”, is one of the most important tenets of investing. Diversification can balance risk and returns for investors. If you are over-invested in one particular asset class, you may end up either taking too much risk or accept too little returns. Through asset allocation you take optimal risks to get the right returns needed for your financial goals.
How asset allocation diversifies risk?
Asset classes like equity, commodities, fixed income, etc. have varying investment cycles. There is a low or, sometimes even negative correlation in returns of two or more asset classes. The chart below shows the annual returns from each asset class viz. equity (represented by Nifty 50 TRI), debt (represented by Nifty 10-year benchmark G-Sec index) and domestic prices of Gold and Silver (based on MCX spot prices). You can see in the chart below that equity and gold are usually counter-cyclical to each other, i.e. Gold outperforms when Equity underperforms and vice versa. Further, there is a low correlation between debt and the other asset classes. Diversifying your portfolio across asset classes limits downside risk when a particular asset class underperforms.
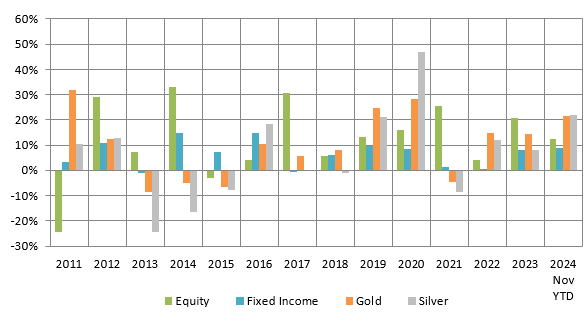
Source: National Stock Exchange, MCX, Advisorkhoj Research, 01.01.2011 to 30.11.2024. Equity: Nifty 50 TRI; Fixed: Nifty 10-year benchmark G-Sec Index; Gold: INR price of Gold (MCX), Silver: INR price of Silver (MCX). Disclaimer: Past performance may or may not be sustained in the future. The chart above is purely for investor education purposes and should not construed as investment recommendation.
What are Hybrid funds?
Hybrid Funds are mutual fund schemes that invest in multiple asset classes, viz. equity, fixed income, commodities etc. A 1986 study done in the United States showed that asset allocation is the most important determinant of portfolio performance (source: Brinson, Hood, Beebower, Financial Analyst Journal 1986). There are different types of hybrid funds with different asset allocation strategies which provide solutions for a wide variety of investment needs and a range of risk appetites.
Hybrid funds categorization as per SEBI
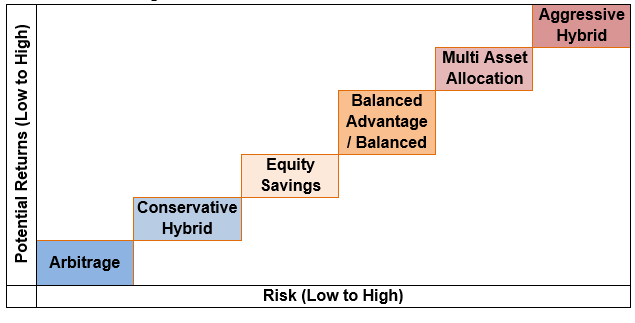
Arbitrage funds: These funds follow arbitrage strategy by exploiting the price differences of the same underlying security in different equity market segments e.g. cash market and derivative market. These funds have a minimum 65% allocation to equity and the balance in money market or debt instruments. These schemes have the lowest risk profile among all hybrid schemes, comparable to liquid or ultra-short duration debt funds. They are suitable for conservative investors with very short investment tenures – few days or months. Investors should note that arbitrage funds may charge exit load for redemption within 30 days and plan their investments accordingly. These funds enjoy equity taxation. Short term capital gains (holding period of less than 12 months) are taxed at 20%, while long term capital gains (holding period of more than 12 months) are tax exempt up to Rs 1.25 lakhs and taxed at 12.5% thereafter.
Conservative Hybrid funds: Investing 10 to 25% of their assets in equity or equity related securities and 75 to 90% of their assets in debt and money market instruments, the primary investment objective of these schemes is income generation. However, the equity component of the scheme can give significant returns over a long investment horizon. These schemes are suitable for investors with conservative or moderately low risk appetites. Conservative hybrid funds are taxed like debt funds. Capital gains (irrespective of holding period) are added to the income of the investor and taxed as per the income tax slab of the investor.
Equity Savings funds: These funds invest minimum 65%-90% of their assets in equity or equity related securities (including derivatives) and minimum 10% and a maximum of 35% of their assets in debt or money market instruments. These funds are allowed to hedge their equity exposure by using derivatives, thereby reducing the portfolio risk. Investors should read the SID before investing as these funds are required to state their minimum hedged and un-hedged exposure in their scheme information document (SID). The investment objectives of these funds are capital appreciation and income generation. These funds are suitable for investors with moderate risk appetites. Equity savings funds enjoy equity taxation.
Dynamic Asset Allocation or Balanced Advantage funds: The Dynamic Asset Allocation or balanced advantage funds adopt a strategy of dynamic asset allocation within the upper or lower asset allocation limits for asset classes. Balanced advantage funds increase or decrease their equity allocation according to market valuations. Most balanced advantage funds increase their equity allocation (decrease their debt allocation) when equity market valuations are lower and vice versa – these funds follow anti-cyclical strategy. The investment objective is capital appreciation and income generation, while reducing downside risk in volatile markets. These funds are suitable for investors with moderately high-risk appetites who want to avoid high volatility. Balanced advantage funds can be taxed as equity or debt or as hybrid funds (with equity allocation between 35 – 65%) depending on the asset allocation of the scheme. Short term capital gains (holding period of less than 24 months) of hybrid funds with equity allocation between 35 – 65% are taxed as per the income tax rate of the investor. Long term capital gains are taxed at 12.5%. Read the scheme information document or consult with your mutual fund distributor to understand the taxation of your balanced advantage fund.
Balanced funds: These funds have to invest 40 – 60% in equity and 40 – 60% in debt as per SEBI. Currently, there are only 2 balanced funds. As per SEBI’s rules, an asset management company can offer either a balanced fund or an aggressive hybrid fund (to be discussed later). Short term capital gains (holding period of less than 24 months) in balanced funds are taxed as per the income tax rate of the investor. Long term capital gains are taxed at 12.5%.
Multi Asset Allocation funds: These funds invest minimum 10% in each of the minimum 3 asset classes (e.g. equity, debt, gold, silver, international, real estate etc.). Different assets have different performance trajectories in different market phases. These funds are suitable for investors who want exposure to multiple asset classes like commodities, international equities etc. along with equity and debt, with the expectation of relatively stable performance across different market conditions and lower downside risks. Multi asset allocation funds can be taxed as equity or hybrid funds (with equity allocation between 35 – 65%) depending on the asset allocation of the scheme. Read the scheme information document or consult with your mutual fund distributor to understand the taxation of your multi asset allocation fund.
Aggressive Hybrid funds: With the primary objective of capital appreciation, these schemes invest 65 to 80% of their assets in equity or equity related securities and 20 to 35% of their assets in debt and money market instruments. Aggressive hybrid funds are suitable for investors with moderately high to high risk appetites. Aggressive hybrid funds enjoy equity taxation.
Product Positioning - Risk Return Profile
Taxation of hybrid funds
The Government made a number of changes to capital gains taxation in the Union Budget of 2024. The table below summarizes the taxation of hybrid funds. Please note that this table is for general guidance – different schemes within the same category may have different tax consequences.
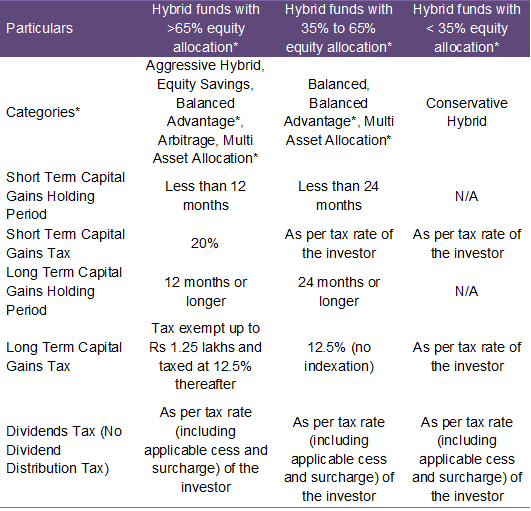
*Investors should consult with their financial advisors to know the tax treatment of their hybrid funds. Disclaimer: The table is purely for the purpose of investor education to illustrate the taxation changes of hybrid funds. Investors should not use to assess the taxation of their mutual fund transactions. Different schemes within in the same fund category may have different taxations. You should consult with your financial or tax advisor to know the tax consequences of your mutual fund transactions.
Why invest in hybrid funds now?
The market has bottomed out in November 2024 and is in a consolidation phase now. The sharp correction has brought down valuations but concerns remain due to corporate earnings outlook. The Reserve Bank of India has revised India’s GDP growth outlook for fiscal year 2025 down to 6.6% (source: RBI MPC 6th December 2024). From the long term perspective, India is in a macro sweet spot due to moderating inflation, narrowing fiscal deficit, strong forex reserves, improving asset quality of banks and healthy corporate balance sheets. However, headwinds from strong dollar and short term growth outlook may cap the gains. In these conditions, asset allocation will play an important role in providing stability to your portfolio. From a long term perspective as well, asset allocation can balance risk / returns in achieving your financial goals. Hybrid funds provide tax efficient asset allocation solutions for investors with different risk profiles and investment needs. These funds can also be suitable for new investors who do not have the experience of navigating through rough weather in financial markets.
Consult a mutual fund distributor or your financial advisor to understand which hybrid funds can be suitable for your risk appetite and investment needs.
Mutual Fund Investments are subject to market risk, read all scheme related documents carefully.
RECOMMENDED READS
The information being provided under this section 'Investor Education' is for the sole purpose of creating awareness about Mutual Funds and for their understanding, in general. The views being expressed only constitute opinions and therefore cannot be considered as guidelines, recommendations or as a professional guide for the readers. Before making any investments, the readers are advised to seek independent professional advice, verify the contents in order to arrive at an informed investment decision.
Mutual Fund investments are subject to market risks, read all scheme related documents carefully.
Quick Links
Follow Nippon India MF
More About Nippon India MF
POST A QUERY






